Human Robotics at the University of Alicante has almost twenty years of experience in research in design and control of robotics systems. This research have been developed in collaboration with different European Universities and research groups such as Lagadic (INRIA, Rennes, France), SIGMA (Clermont-Ferrand, France), Industrial Systems Institute (ISI, Greece), Onboard Space Systems (Luleå University of Technology, Sweeden).
The design of robot allows not only to determine the adequate kinematic and dynamic properties of a robot for a given application, but also its construction and experimentation. The design of robots is a practical research line which allows the design, control and construction of robots in different scenarios such as humanoid robots, social robot, industrial robotic arms, field robotics, etc. Additionally, the implementation of robots with better dynamic characteristics than those existing in the market, can facilitate the creation of future companies within this emerging field.
Visual Servoing
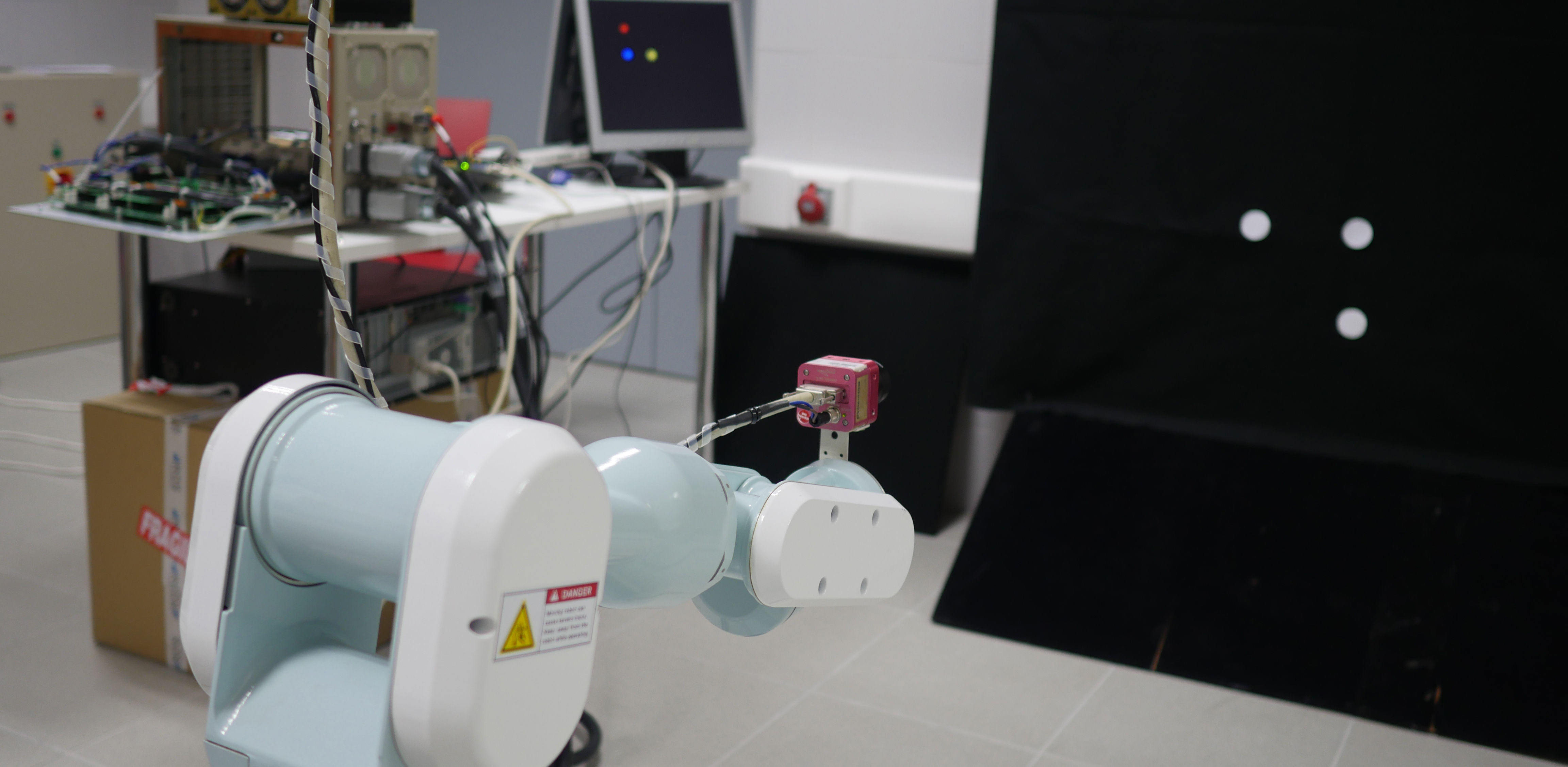
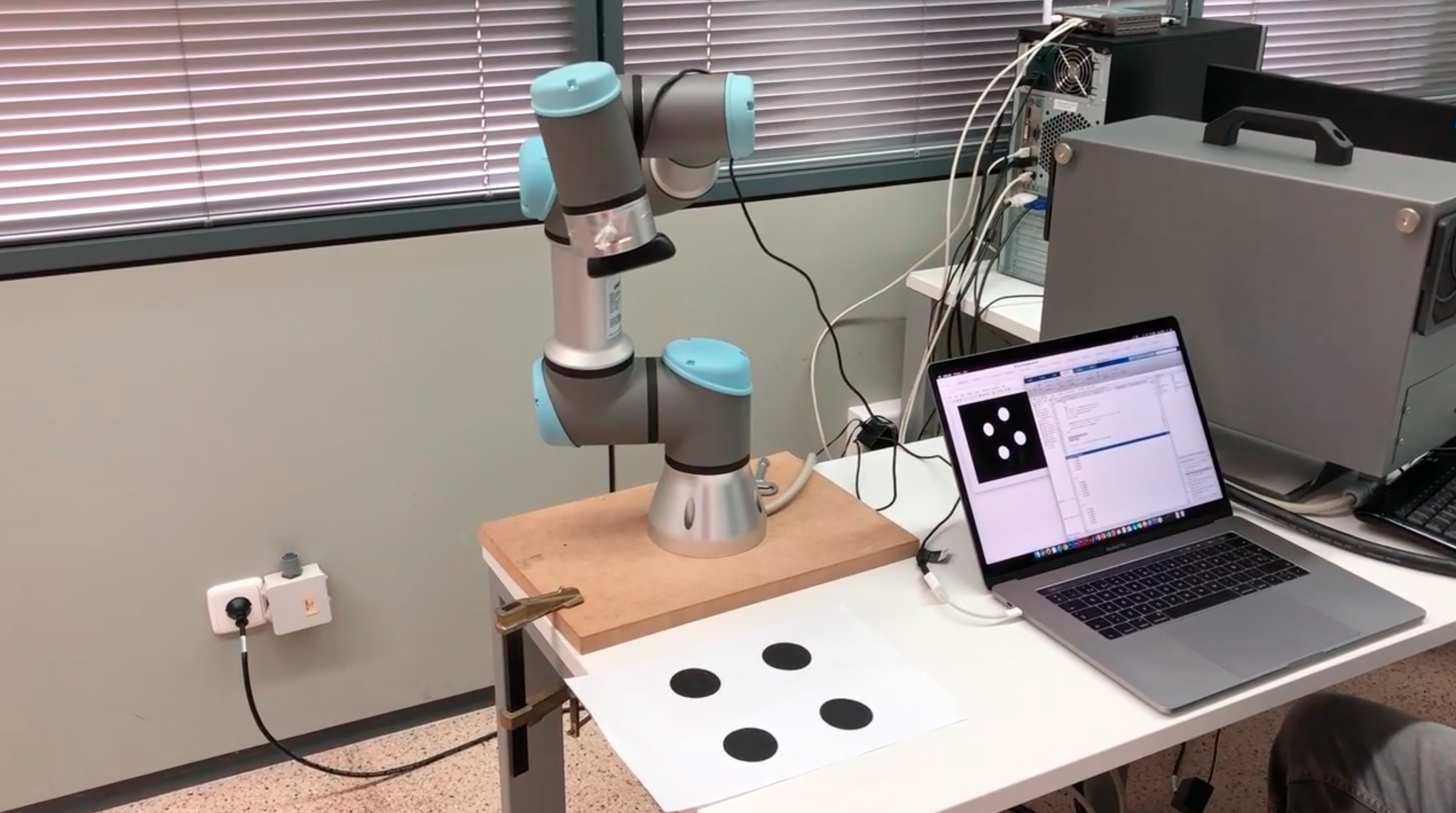
Visual servoing allows the guidance of robots by using visual information. HUman Robotics research group have been focused in this topic during the last decade. Computer vision is one of the research topics that currently has a broader spectrum of potential industrial applications, and that in the future will still acquire greater relevance. Proof of this are the efforts made by the main research centers around the world and the interest that the industry demands in these applications. Its special properties make it capable of capturing a large amount of information from its environment to allow the guidance of the robot without the need to have a thorough prior knowledge of the workspace. Therefore, visual servoing allows for robot guidance using visual information or visual characteristics extracted from the environment.
Force control, manipulation and interaction control
Force control is required in different application areas to increase dexterity of robotic mechanisms in industrial environment (for example, assembly, debarring, polishing, handling flexible parts, etc.) and also in non-industrial environment (hospital, home, town, space, etc. for service, maintenance, welfare, entertainment, etc.). Different approaches have been proposed until now to control the robot interaction with the workspace: hybrid approaches, impedance control, indirect control, parallel control, etc.
A fundamental requirement for the success of a manipulation task is the capability to handle the physical contact between a robot and the environment. Pure motion control turns out to be inadequate because the unavoidable modeling errors and uncertainties may cause a rise of the contact force, ultimately leading to an unstable behavior during the interaction, especially in the presence of rigid environments. Force feedback and force control becomes mandatory to achieve a robust and versatile behavior of a robotic system in poorly structured environments as well as safe and dependable operation in the presence of humans. The researchers of HUman Robotics have been working in new force control approaches to improve the performance of the robots in interactions tasks.
The use of humanoid robots in social environments requires not only the use of force control but also to develop complex control apparoaches in dexterous manipulations tasks performed with robotic hands.To achieve a human like grasping with a multi-fingered robot hand, the grasping force should be controlled without using information from the grasped object such as its weight and friction coefficient.
Human Robotics Group - University of Alicante
Design and Control
of Robots
Advanced mechanical design of robotic devices and kinematic - dynamic control performance
Contact us
-
Human Robotics
UA Polytechnic School 3
Physics, Systems Engineering and Signal Theory Department
University of Alicante
Ctra San Vicente del Raspeig s/n
San vicente del Raspeig
03690 Alicante, Spain. -
(+34) 965 903 400 Ext. 1094
-
huro@ua.es
-
Week Days : 09:00 – 18:00
Saturday, Sunday : Holiday